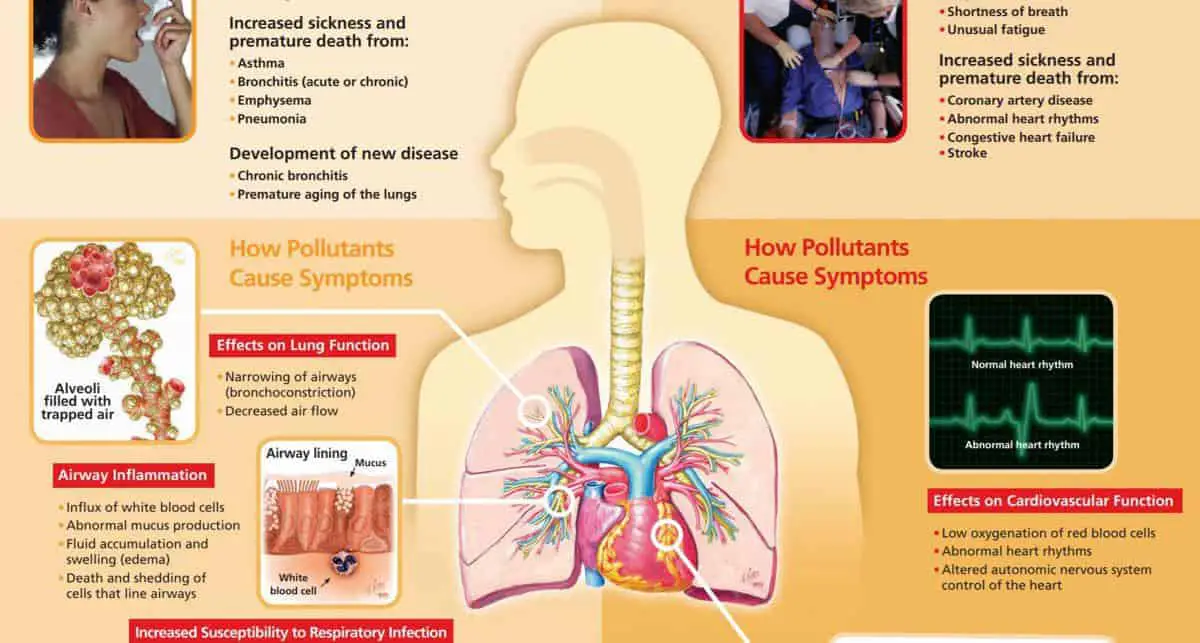
We all want to remain healthy but in many countries air pollution is now a hidden problem that is leading to disease, disability and may even be making us age faster than we would do naturally.
Particulate air pollution is the major determinant of air quality except for some localized areas of the U.S. where there is a concentration of chemical plants such as “cancer alley” along the Mississippi. In the United States particulate air pollution now ranks as the 15th most important cause of loss of healthy life years, with 930,000 years of life lost every year. It is also the 15th most important cause of disability.
It comes in many forms-particulate matter, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, lead, ground-level ozone, and carbon monoxide. Particulate matter can be caused by the combustion of hydrocarbons, brake pads, tires and plastic pollution.
In the United States alone, 200 million people live in areas where the pollution level is above the EPA standards. So almost 2 out of every 3 Americans is exposed to significant air pollution according to the current EPA definition. However, according to the 2021 WHO definition and 2020 US Govenment statistics 98% of Americans live in areas which are above safe limits, as I discuss below.
It was reported “the simple act of breathing is killing 7 million people per year”-Guardian newspaper and the WHO referred to air pollution as “the new smoking”.
On average fine particle air pollution leads to premature aging, premature death, asthma, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, heart attacks and strokes. Dementia, parkinson’s disease and visual impairment are increased. Also particles damage the unborn child and children after birth.
Recently it has become clear that the adverse health effects of airborne particles occur at very low levels, raising the issue of should everyone have an air purifier? There is also evidence that children and the elderly may be particularly vulnerable.
The Health Affects of Airborne Particles Are Seen at Very Low Levels-should everyone now breathe purified air for at least part of the day?
Airborne particles have been shown in clinical or epidemiological studies, often multiple studies, to cause-
- Coronary heart disease-heart attacks
- Strokes
- Premature aging of the lungs
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Pneumonia
- Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Diabetes
- Skin problems including skin aging
- Autoimmunity
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Dermentia
- Cognitive decline-decrease in thinking ability
- Parkinson’s disease
- Vision impairment-age related macular degeneration and glaucoma
- Impairment of sense of smell
- Sleep disturbance
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Increased risk of psychiatric problems
- Decrease in fertility
- Increased miscarriage
- Exposure during pregnancy linked to neurological problems, asthma, lower IQ in child
- Children-lower intelligence and delayed psychomotor development, faster decline in cognitive function in adulthood
- Children-chest infection, asthma
- Children-increased obesity
- Children-increased psychiatric problems
- Children-death rate increased
- Premature aging?-ultrafine particles speed up several processes involve in aging
- Premature death
Types of Air Pollution
- Particulate pollution Most of the health effects of air pollution are because of fine and ultrafine particles (PM 2.5). PM 2.5 are particles less than 2.5um in diameter. Over 95% of the particles in the air are less than 0.1 µm in diameter-these are ultrafine particles. Both PM2.5 and ultrafine particles can be inhaled deeply into lung tissue, and the ultrafine particles are even small enough to enter the bloodstream. When they enter the bloodstream, they not only affect the blood vessels but can be deposited in other organs. They occur naturally but are also produced by combustion of fuel, domestic wood burning, forest fires, tire particles, brake dust and also asphalt related emissions. The ammonia released by manure from livestock causes the formation of PM 2.5 particles in the air, and this is currently responsible for 20,000 deaths per year in the US.
- Nitrogen oxides-are caused by motor vehicle emissions and industrial processes. Nitrogen oxide irritates the lungs and affects T lymphocytes-part of the immune system. Short-term exposure to nitrogen oxide has been linked to increased overall mortality and mortality from cardiovascular and respiratory causes.
- Sulfur oxides-are caused by motor vehicle emissions and industrial processes. Sulfur dioxide irritates the airways in the lungs.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOC)-are produced by the combustion of fossil fuels and evaporation from household chemicals such as glues and paint. They have been associated with cancer in humans.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)-formed during combustion of gasoline and during power generation. Incomplete burning of organic matter material during forest fires creates PAH. They are also found in particulate matter. Inhalation of PAHs is an important risk factor for lung cancer.
- Ozone (at ground level)-an atmospheric gas with 3 oxygen molecules bonded together. Formed when chemicals emitted by cars, power stations and chemical plants as well as some consumer goods escape into the atmosphere. In the presence of sunlight, a chemical reaction can take place leads to the formation of ozone. Ozone irritates the airways in the lungs. Due to its insolubility in water, it can penetrate deep into the lungs. Higher ozone levels have been associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%). Similarly, there is an increase in respiratory (1.13%) and cardiovascular (0.45%) deaths. This was only seen during the warm period of the year, not winter. Ozone also reacts with skin/skin products to create a personal chemical pollution cloud. Higher levels of ozone are associated with pneumonia. Ozone may also be carcinogenic.
- Plastic Particles-The whole of the earth is now covered in plastic particles. These as well as cellulose fibers from plants have been found in human lung tissue.
- Carbon Dioxide-a man-made air pollutant created particularly by burning fossil fuels. At higher levels, usually in confined spaces/offices, this is associated with impaired thinking ability (please see section on Cognition below).
- Benzoapyrene-formed by burning fossil fuels is linked to the most severe form of childhood asthma–non atopic asthma.
Forest fires are a cause of fine particulate PM2.5 air pollution, but they can also cause the release of dioxins into the environment. These accumulate in the food chain in products such as meat and dairy products, especially the fatty tissue of animals. They have been associated with immune endocrine and nervous systems problems with infertility and cancer when the exposure is long term. These fires seem to be an increasing problem due to climate change.
Some indoor air pollution does not simply come in from the outside. A proportion of household air pollution is generated within the home itself from cooking, burning wood in fires and the use of chemicals for cleaning and in other products such as cosmetics.
Respiratory Problems-Damage to the Airways, Premature Lung Aging and Pneumonia are Problems
One of the principal organs vulneragel to the health affects of airborne particles are the lungs in with the effects are the causation of diseases and an increase in the speed of aging of the lungs.
Diseases of the Lungs
The lungs and skin form the surfaces of the body in direct contact with air pollution. So it is no surprise that air pollution is associated with respiratory disease and increased skin aging. In the lungs air pollution is associated with emphysema (destruction of lung tissue) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (damage to airways). Both of which can cause severe disability and premature death. Air pollution accelerates the progression of emphysema as much as a pack a day of cigarettes.
The study used 15,000 CT scans thousands of people over as long as 18 years. Baseline levels of oxides of nitrogen and PM 2.5were also linked to increased emphysema over 10 years. Ozone was also associated with a faster decline of lung function in those with emphysema.
Poor air quality has also been linked to exacerbations of asthma. Air purifiers particularly suited to respiratory disease are listed in this article which outlines a selection of medical grade air purifiers. Asthma can also be helped by humidification as I outline in this article.
Air pollution is also associated with an increased incidence of pneumonia. The most common cause of severe pneumonia is pneumococcus. Macrophages, cells which are part of the immune system, have their function impaired by exposure to diesel exhaust particles which may explain this.
ER visits for breathing problems increase with air pollution. Higher ozone levels were associated with increased ER visits for asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pneumonia. Another form of pollution, fine particulate, PM 2.5, pollution was linked to an increased incidence of asthma, acute respiratory infection and pneumonia. The effect of particulate matter particularly affected children but was also seen in adults up to 65 years old.
Lung cancer is also associated with air pollution-please see the section on cancer below.
I compared a study in which sham air purifier filtration with true filtration on average decreased indoor PM 2.5 concentration by 72.4%. This lowered small airway resistance by 20% and larger airway resistance by 7.4%. So using an air purifier can lead to improved airway mechanics.
Air purifiers particularly suited to respiratory disease are reviewed here.
Premature Aging of the Lungs
A study in 303, 887 individuals showed that PM2.5 particulate air pollution levels were associated with a faster decline in lung function in people without respiratory disease.
The shortness of breath and lack of access towards the troubles us all as we age was thought to be due to reduced elasticity in the lungs with age. However, a study based on CT scans of postmortem specimens of one suggests that it is the reduction in the number of terminal bronchioles, the very smallest airways, that causes this. It is interesting to note that this is where ultrafine particles are deposited. The number of these terminal bronchiloles decrease by 50% between the age of 40 and 80 years old. So, it is possible that the decline in lung function with age is due to ultrafine particle deposition and damage to these smallest of airways. So part of what we now think of as aging may simply be damage to the lungs from persistent particle deposition-even in normal air there are 2 million ultrafine particles per liter. For further details on ultrafine particles please see this article-“Airborne Ultrafine Particles-do they accelerate aging“.
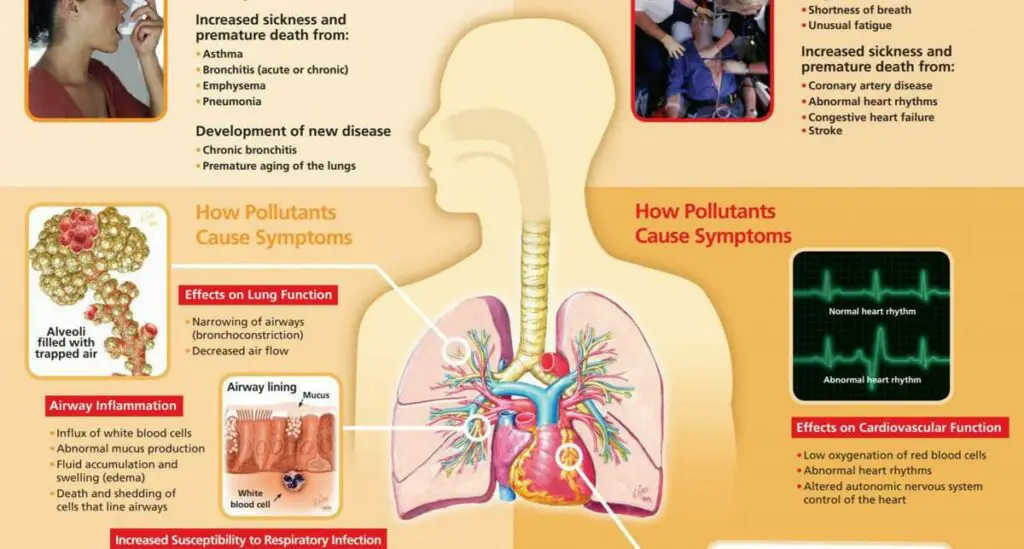
Cardiovascular Problems-Heart Attacks, Cardiac Arrests, Strokes and Mortality Increase With Air Pollution
Because small particles can enter the bloodstream, they can lead to effects on the blood vessels. Small particles, PM 2.5, impair blood vessel function as well as increasing markers of oxidative stress and inflammation. Both are linked to increased speed of aging. These small particles also damage the arteries, as shown by an increased amount of calcification in the wall of the artery. This calcification is a marker for underlying atherosclerosis, the most common arterial disease. It is involved in almost all heart attacks and the vast majority of strokes.
A study of young adults, average age 23, from Mexico City showed that there were 10 billion combustion and friction derived pollution particles per gram of heart tissue present in the heart muscle! These particles were found to have entered the body and be able to catch a ride on the red blood cells, then be transferred to any activated endothelial cells lining the blood vessels and then enter the heart tissue. They were found inside the heart muscle cells in the mitochondria (power generators).
The particles were also found in the endoplasmic reticulum – protein generating machinery of heart muscle cells. So pollution particles have been demonstrated to penetrate even within individual cells within our body!
Coronary Heart Disease
One major health affects of airborne particles is on the cardiovascular system, and coronary arteries in particular. In a Chinese study, long-term exposure to particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide was related to the development of coronary artery disease. Household particulate matter (PM 2.5) was linked to higher blood pressure in all the Chinese women. The systolic blood pressure increased by 3.5 mmHg, the diastolic by 1.3 mmHg there was also a higher pulse pressure 2.9 mmHg. These are all quite significant increases or any you consider that the heart is beating a hundred thousand times a day. Exposure to traffic related air pollution is been shown to lower levels of high-density lipoprotein. This reduction is associated with an increased risk from cardiovascular disease.
Also, exposure to air pollution has been linked to coronary artery calcification. This was seen in 6800 participants in the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution. It was found that higher PM 2 concentrations were associated with an increased buildup of calcification in coronary arteries. Higher nitrogen oxide levels were also related to an increase in coronary calcification. Other studies have shown that the degree of coronary artery calcification correlates with all likelihood of having a heart attack.
Air pollution at work, particularly from particulates, pesticides or metals, has been linked to cardiac abnormalities. The longer workers were exposed to the pollution, the more likely they were to have cardiac abnormalities. Occupational exposure to burning wood was associated with 3% lower pumping function of the left ventricle the main pumping chamber of the heart.
In a study of 39,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, they were found to be related to PM 2.5 particulate air pollution.
Stroke
PM 2.5 particulate pollution was found to lead to a 74% increase in the risk of stroke in people who had never smoked. In another study traffic pollution at the residential address as assessed by PM 2.5 was linked to an increased incidence of stroke. This was even at PM 2.5’s in the range of 5.8 to 9.2 mcg/m³, this is at levels lower than European Union, WHO and EPA guidelines. Hemorrhagic strokes were increased in postmenopausal women by short-term exposure to nitric oxide. Having a stroke and then made developing dementia more likely.
A review of 93 studies showed that short-term air pollution also increased the risk of stroke. Fine particles (PM2.5), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone all increased the risk. The increase was most substantial on the day of exposure. The effect was longest lasting for PM2.5 particulate pollution.
Strokes were also seen with increasing frequency in 943 relatively young men (70 years old) who were exposed to PM2.5 fine particulate pollution. This was especially a problem within 75 meters of a road. The study used MR brain scans to determine if someone had had a stroke. Those in the highest quarter of pollution levels had a 46% increased incidence of stroke compared to those in the lowest. In addition, they found that each 2ug/m3 increase in PM 2.5 concentration led to a decrease in brain volume equal to one year of aging!
Air pollution may account for 19% of all cardiovascular deaths and 21% of deaths from stroke.
High blood pressure may alter the body’s response to poor air quality. In an animal model it shifted the body’s response to air pollution away from a parasympathetic, “calming”, activation to activation of the sympathetic nervous system, a “fight-or-flight” response.So seems that the status of the cardiovascular system modifies the response to air pollution.
Particulate air pollution activates blood cells in the bone marrow this activation is associated with inflammation in the walls of the arteries. These inflamed arterial walls are then more unstable. This leads to cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. This effect accounts for 27% of the linkage between air pollution and cardiovascular events. It is seen even within the range of particle pollution deemed safe. Or as one of the authors put it “no level of air pollution can truly be considered safe“.
Further evidence for arterial inflammation being the link and possibly caused by stimulation of the white blood cell system was seen in another study.
Once the walls of the arteries are inflammed they are more unstable and prone to breaks in the inner layers of the walls. This leads to the formation of a clot in the artery which then can cause a heart attack or stroke.
Using an air purifier in one study reduced von Willebrand factor by 26.9%, 24 hours after the end of the air filtration. Von Willebrand factor is a blood coagulation factor and a reduction indicates a reduced risk of thrombosis, which is a mechanism involved in both heart attacks and strokes. So this is one indication that an air purifier may be effective at reducing cardiovascular risk.
Cancer-a Few Cancers Increase With Air Pollution
Particle Pollution and Cancer
A long-term study over 16 years found an increased instance of lung cancer in areas that were reliant on coal-fired power stations for generating electricity. A study looking at 456,000 people found that those non-smokers in areas with higher PM 2.5 and nitrogen oxide levels in the air and a 60% increase in the incidence of lung cancer. The incidence of lung cancer increased with particle count even at low levels that we currently consider safe.
That there is a risk of developing breast cancer from air pollution is supported by a study of 57,000 women. There was an increased risk of breast cancer in those who were living close to a major roadway. The hazard ratio was 1.85, almost doubled by increased exposure to higher levels of PM 2.5 particles.
There is also an association between ultrafine particles and brain cancer.
Also studies in animals and human cells have shown that ultrafine particles cause or can carry substances which cause mutations and stimulate tumour formation.
Chemical Pollution and Cancer
However, particles are not the only problem and benzene exposure can cause leukemia and is associated with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Benzene is found in petroleum products and is used in the manufacture of chemicals. Air pollution has been linked to bladder cancer.
The National toxicology program lists 15 PAHs, as carcinogens.
The data is quite clear that one of the health problems from air pollution is causing cancer, at least for lung cancer. Air pollution also seems to cause bladder cancer and quite possibly breast cancer although the data are more limited.
Diabetes, Immune Problems, Kidney Failure, and Other Problems Increase With Particulate Pollution
Air pollution is linked to-
- Diabetes mellitus prevalence morbidity and mortality. One study showed that exposure to fine particulate matter, PM 2.5, increased insulin resistance in mice. Their DNA was altered-epigenetic changes, but fortunately this was reversible when the particulate matter is removed from the air.
- Allergic rhinitis
- Allergic sensitization
- Skin problems – urticaria, acne and skin aging
- Autoimmunity
- Osteoporosis
- Conductor pipe tests, dry eye disease, blepharitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Renal impairment – decreased glomerular filtration rate
Brain Shrinkage, Dementia, Parkinsons Disease and Blindness All Increase
Particulate air pollution has widespread effects on the brain. These include brain shrinkage, dementia, and possibly Parkinson’s disease and depression.
One study found that breathing higher levels of fine particle pollution was linked to more brain shrinkage. For each 3 mcg/m³ increase in particulate air pollution exposure the brain shrinkage over 5 years was equivalent to a 24% increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Cognitive (Thinking Ability) Decline
Air pollution both nitric oxide and PM 2.5 has been linked to lower cognitive function, and an increased rate of decline of cognitive function. A study in china found that air pollution reduced cognitive ability so much that it was equivalent to one less year of education!
Conversely, air filters in classrooms increase pupils’ maths and English scores in exams. In a US study higher exposure to particulate matter was linked with over 55-year-old’s making 50% more errors in memory and maths tests. Similarly in a study by Harvard in office workers, PM2.5 concentrations were found to lower cognitive function, “thinking ability”. The effect in the Harvard study was only seen at PM2.5 concentrations above the EPAs recommended limit of 12g/m3.
In China air pollution was found to reduce cognitive ability in children, and also in adults so much it was equivalent to 1 years less schooling. The affect was particularly severe in older adults.
Carbon dioxide, another pollutant from industrialization, is associated with lower cognitive performance. So as we seal our houses for energy efficiency trapping carbon dioxide in our homes and also with rising carbon dioxide levels-we may be slightly less able to think well. Another study also found that both carbon dioxide and volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere within buildings were linked to lower cognitive ability.
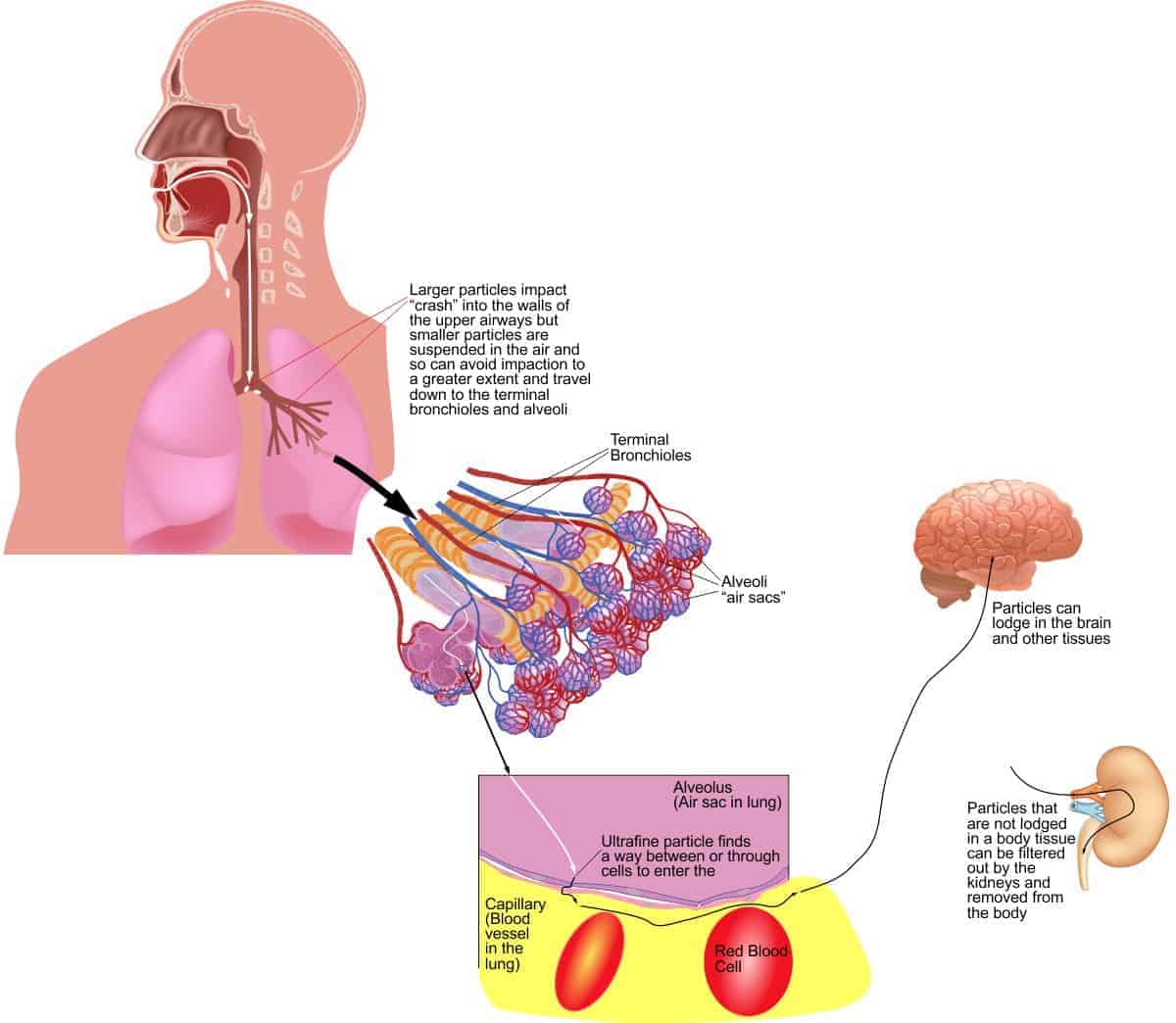
On average, we all have approximately 6,000,000 ultrafine particles in the alveoli of our lungs at all times as we breathe the air. We could reduce this 5-10 fold to 1.2million-600,000 with an air purifier if we use excellent technique. However, there is no definite proof of a long-term health benefit of doing so, yet-as there are no long-term studies. This is “absence of evidence” rather than “evidence of absence” of an effect.
Dementia
In a US wide study of older women living where fine particle levels were above the EPA standards, the risk for cognitive decline increase by 81% and dementia increase by 92%. The same study also looked at transgenic mice, which after 225 hours of exposure to Nano -sized particles over 15 weeks showed increased amyloid deposition in their brains. Specifically, increased alpha-beta oligomers, which caused selective atrophy in the hippocampal (memory bank) cells.
Another study linked air pollution to dementia but only vascular dementia, which increased by 66%, but there was no increase in Alzheimer’s disease.
A study from San Francisco investigated 18,000 people whose average age was 75. The participants all had mild cognitive impairment or dementia. It was found that those in most polluted areas had a 10% increase in probability of their PET scan demonstrating amyloid. Researchers found that even at concentrations of PM 2.5 there were not very high but would be average for San Francisco had an association with amyloid deposition in the brain.
They felt that air pollution should be added to the modifiable risk factors for dementia. A study from Taiwan found a 138% increase in Alzheimer’s disease for each 4.3 mcg/m³ increase in PM2.5 particulate matter above the EPA threshold.
In the Dementia, Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission outdoor air pollution was considered to be one of the risk factors for dementia. Overall, the increased risk of dementia in areas with high traffic pollution was felt to be 10% and from residential wood-burning 60%.
“I have no hesitation whatsoever to say that air pollution causes dementia,” says Caleb Finch, gerontologist and the leader of USC’s Air Pollution and Brain Disease research network, which has completed many of these new studies.
So unfortuately dementia also seems to be one of the health problems from air pollution.
Parkinsons Disease
An experimental study showed that chemicals in diesel exhaust can trigger the clumping of alpha-synuclein. It is the clumping of this protein which is the central mechanism in Parkinson’s disease.
A study from Mexico City examined 186 young people between 11 months and 27 yearsYou are exposed to higher levels of traffic pollution. Markers of Alzheimer’s disease, motor neuron disease, and Parkinson’s disease were found. There were nanoparticles with a high iron, aluminum and titanium in the brainstem. The iron and aluminum particles were strikingly similar particles created by internal combustion engines and braking systems of motor vehicles.
Researchers commented on the association between the presence of particles and damage to the cells, and in particular their mitochondria. No similar changes were seen in the brains of age and gender-matched controls living in lower pollution areas.
More data is needed, but air pollution may well be a factor in the causation of Parkinson’s disease.
Brain Tumors and Air Pollution
Ultrafine particles were found in brains in 2016. A study from Canada covering 1.9 million people has linked air pollution to the incidence of brain tumors. There was a link between ultrafine particle exposure and brain tumors. PM 2.5 and nitrogen dioxide exposure were not linked to brain tumors.
Visual Impairment
Air pollution has been associated with the 2 leading causes of visual impairment as we age, namely age related macular degeneration and glaucoma. Approximately 5% of the population over the age of 65 years old have macular degeneration. In this condition, the photoreceptor cells in the retina deteriorate or are damaged by the growth of new blood vessels.
So it is the most common cause of irreversible blindness in developed countries. 1 in 8 people will have developed AMD by the age of 80. Recent studies show that an increased number of particles in the air are linked to an increased likelihood of developing AMD.
A study scanning the retinas of more than 50,000 people found a 8% higher risk of AMD for each 1 mcg/m³ increase in PM 2.5. So for a 12 mcg/m³ increase in PM 2.5 the incidence of AMD would be expected to double. Another study showed a similar finding.
In glaucoma pressure builds up in the eye and the depression damages the nerve cells in the retina that transmit the signals from the photoreceptors to the brain. Similarly, another study found a link between PM 2.5 air pollution and glaucoma. Both the incidence of glaucoma and its severity increased with increasing particulate air pollution.
Impairment of Sense of Smell
Exposure to fine particle pollution, PM 2.5 is also associated with loss of sense of smell.
Sleep
Sleep efficiency is decreased in with high air pollution both PM2.5 and nitric oxide. Disturbance of breathing such as sleep apnoea is one mechanism. Another mechanism is that ozone may also cause neuroinflammation, and this inflammation of the brain leads to sleep disturbance.
Mental Health is Worse with Air pollution
A study in more room in over 80 found that long-term exposure to nitrogen dioxide or fine particular air pollution is associated with more depressive symptoms. This was however a relatively small effect.
Another study analyzed 14 studies with data from 684,859 participants investigating the link between PM 2.5 ambient air pollution and depression. It found a 19%increased risk of depression, but the slightly increased risk of suicide was not statistically significant. There seems to be a cumulative effect over time with those exposed to pollution longer more likely to suffer depression. A study from China looking at social media showed that happiness declines when air pollution increases.
In the nurses’ health study, 70,271 nurses were assessed for anxiety and past exposure to fine particulate matter. There was found to be an association between higher levels of exposure to particulate matter and increased anxiety.
Air pollution has been associated with an increased risk of psychiatric problems. Particularly living in polluted areas early in life was associated with mental disorders later.
So there seems to be an increased incidence of mental health problems with increasing air pollution.
Aspirin or other non-steroidal anti inflammatory medication may protect against this decline. However because of their side effects and the need for further studies this approach cannot yet be recomended.
Obesity Increases with Air Pollution?-More Studies Needed
In adults, the effect of air pollution on obesity is not clear, and further studies are needed. One review found that, in 44% of studies linked air pollution to increased obesity, 44% of studies found that it makes no difference, and 12% of studies find that it is linked to reduced obesity.
Air Pollution Decreases Fertility
A decrease in ovarian reserve, the number of resting follicles in the ovary, is related to particular matter and nitrogen dioxide exposure. Also, in male mice sperm production is reduced in the presence of fine particulate PM 2.5 air pollution. A study of 18,000 couples in China found that those living in areas with higher pollution had a 20% greater risk of infertility. Each 10 mcg/m³ increase in PM 2 pollution was associated with an 11% increase in infertility. Also a study of 600 women, air from an infertility clinic in the United States showed a lower number of maturing eggs in those in areas with fire pollution.
Nitrogen dioxide pollution is also been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage as much as smoking.
Pregnant Women and Air Pollution-Bad Effect of Air Pollution on Mother and Foetus
It is becoming increasingly apparent that air pollution can reach the placenta and have effects on the baby. Women who intend to have a baby or who are already pregnant may wish to consider using air purifiers at home.
Nitrogen dioxide in air pollution increase the rate of miscarriage. Nitrogen dioxide and PM 2.5 air pollution has also been associated with lower weight of the baby at birth. It is becoming apparent that ultrafine particles (UFP) may damage the development of the fetus. Exposure to UFP can constrict blood vessels, which lowers blood flow to the uterus and placenta, so affecting the fetal development. In a study investigating the effect ultrafine particles on pregnant rats showed that the most vulnerable times when the first 3rd and the last 3rd of pregnancy.
So, one exposure to pollution later in pregnancy can alter the fetus with consequences that last into adulthood.
Placentas from 15 pregnancies were examined in one study. All the women had been exposed to air pollution in London above the safe limit for particulate matter. Black particles which resembled particulate matter from pollution were found in placental cells from ALL 15 women. The particles were thought to come from fuel combustion and vehicle brake wear. In addition, carbon particles from particulate air pollution have been found in the fetal side of the placenta.
Hypertension, raised blood pressure, in pregnancy has related to traffic related pollution. Increased blood pressure during pregnancy is linked to increased fetal and maternal mortality, preterm birth and low birth weight.
Exposure of the mother during pregnancy to PAH has been associated with various prenatal and childhood neurological problems including brain development attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder as well as slower processing of information.
There may be twice the risk of having a child with autism if the mother is exposed to high levels of PM 2.5 during pregnancy – particularly towards the end of pregnancy.
Prenatal exposure to particulate matter has been associated with babies with lower birth weight and lower IQ.
Also exposure to ultrafine particles during pregnancy has been linked to asthma in the children when born. In fact the scientists who did the study said that the fetus was “exquisitely sensitive” to oxidative stress that ultrafine particle pollution can produce (please see below). Prof Rosalind Wright is quoted as saying that she asks all her expectant mothers to consider taking anti-oxidants as these have been shown to reduce inflammation caused by particle pollution.
Mothers exposed to high levels of nitrogen oxide, nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy had a higher risk of having babies with neural tube defects.
Nanoparticles from the toner of laser printers and was found in rats to alter gene expression. This alteration in genes was linked to cardiovascular neurological and metabolic disorders. These genetic changes could potentially be passed down to the next generation.
One study found that if non-smoking mothers were exposed to secondhand smoke their children had epigenetic changes. These genetic changes were in regions of DNA that are involved in development, brain function and the development of cancer.
Children are Damaged by Particulate Air Pollution
Evidence that air pollution permeates all parts of a child’s body was seen in a study where carbon particles from air pollution were found in the urine of children. This is evidence that like the rest of us, when we breathe in particles if they’re small enough, they can get into the deepest parts of our lungs and enter our bloodstream. The kidneys are constantly filtering out particles so that they end up in the urine. In this way the level of particles in the blood does not just keep increasing as new particles enter the bloodstream from the lungs but reaches a plateau.
Brain
Fine particulate air pollution is related to delayed psychomotor development and lower child intelligence. Particulate exposure at relatively low levels has been shown to alter brain structure in children. This was shown using MRI scans from 11,000 children aged 9 and 10 from cities in the United States. Areas of the brain associated with emotion were larger whereas other areas associated with thinking skills were smaller.
Air pollution as a child seems to affect the rate of decline in cognitive function with age. In one study, those with higher pollution levels in childhood had a faster rate of cognitive decline through to the age of 70 years old.
As mentioned above in the section on cognitive ability, children who breathe air with less pollution do better in exams.
Lungs
A study from California recruited 1759 children at an average age of 10 years and followed them until they are 18 years old. It was found that deficits in the growth of airflow from the lungs in one second (FEV1) was linked to PM 2.5, nitrogen dioxide, elemental carbon and acid vapor. So this study associated air pollution with poorer lung development.
Children who live in high ozone areas and play sports outside have an increased incidence of asthma. Also children you are exposed to particulate pollution are more likely to develop wheezing and asthma.
Children who live near busy roads have more asthma. If they develop as much higher the levels of pollutants means that they are more likely to develop bronchitis-inflammation of the airways.
Particulate pollution is related to an increased incidence of chest infections in children who are then more likely to miss school. Also short term increases in PM2.5, PM10 and nitrogen dioxide levels all lead to more respiratory problems needing primary care consultations.
Conversely, cleaner air was associated with fewer respiratory symptoms in children.
Obesity
There is evidence of a link between air pollution and childhood obesity.
Mental Health
Psychiatric health is also less good in children exposed to air pollution-they tend to be more anxious. Metabolic changes were found in the brains of 12-year-olds exposed to traffic related air pollution, this correlated with anxiety. There is also an increase in emergency psychiatric presentation by children to hospital with an increase in air pollution. Teenagers living in polluted areas of the 40% increased risk of psychosis. Children from areas with high pollution were 3 to 4 times more likely to have depression at the age of 18.
Childhood air pollution is linked to poorer mental health at age 18.
Increased Aging in Children in Response to Increased Indoor Air Pollution
A study from Europe, by measuring the amount of chemical change of our DNA, investigated the effect of air pollution on genetic age in children. By measuring the number and pattern of methyl groups added to the DNA, our genetic age can be calculated. This is part of a field of science known as epigenetics. There are various forms of these clocks but one, Horvath’s Grim Age Clock can predict when we will die fairly accurately.
In children who are exposed to increased particulate matter indoors or tobacco smoke their epigenetic age was found to be increased. So we can see effects of indoor air pollution on the genetics of children.
Deaths in Children
6.6% of deaths of children aged 1 to 5 years old in the United States and 13.6% in Europe are attributable to fine particulate pollution.
Ultrafine Particles- Do They Speed up Aging?
Ultrafine Particles Have Access to All Tissues in Our Body
Ultrafine particles are those less than 100 nm. They’re found in smog, soot, smoke, some viruses, atmospheric dust, and gases. In open areas they are mainly formed by combustion. Not only is the size important the surface chemistry, charge and composition are also important. Ultrafine particles are small enough to enter the deepest parts of the lung, the alveoli. This is where the air enters the bloodstream, these fine particles can also enter the bloodstream just as molecules of oxygen can. From here they can affect all the blood vessels in the body and even penetrate into the organs such as the brain and heart.
They can directly cross cell membranes into the interior of cells. Here they have direct access to the machinery of the cell including the nucleus.
Nanoparticles formed from presumed brake dust have been found in the brains of people – as outlined in the section above. Also, as outlined in the section about children above Nano particles of carbon from air pollution been found in children’s urine. So they have entered the child through the lungs traveled around the body in the bloodstream and finally been filtered out of the blood by the kidneys.
An interesting study in which volunteers inhaled gold nanoparticles showed the ease with which nanoparticles enter the bloodstream. Gold was detected in the blood in urine within 15 minutes to 24 hours after exposure and even 3 months after exposure was still present. 5 nm particles were found in greater concentration in the body compared to 30 nm particles. Studies in mice showed that Nano particles accumulated following pulmonary exposure in both blood and liver. Again, the accumulation was greater for particles less than 10 nm in diameter.
The particles preferentially accumulated in inflamed vascular lesions in arteries. These lesions tend to be more unstable, with greater tendency to lead to heart attacks and strokes. Also, following inhalation in patients, gold particles were detected following carotid surgery in tissue removed from the carotid artery wall. This would provide a direct mechanism by which ultrafine particles could destabilize arterial walls and lead to the increased incidence of heart attacks and strokes that are seen with increased air pollution.
A systematic review of the literature concerning ultrafine particles and human health was published in 2019. This reviewed 85 original studies and concluded that there were adverse short-term changes in the cardiovascular (heart and arteries) system and inflammatory changes. These effects may be to some extent independent of other pollutants. Clinical studies in which subjects breathed in air with ultrafine particles showed some interesting results.
There was little effect on respiratory function, inflammatory markers on white cells were altered and flow mediated dilation of arterioles was reduced. Much of the information that we have derived from animal studies suggests that ultrafine particles have access to the brain and heart in addition to respiratory systems. These particles have also been found to enter individual cells!
Ultrafine Particles Affect Cellular Processes Known to be Associated with Aging
Numerous toxicological collections of fine particles have been found –
- Impairment phagocytosis (ability of white cells to eat bacteria etc.)
- Crossing tissues and cell membranes
- oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- mitochondrial (the powerhouses of the cells) exhaustion
- damage to protein
- damage to DNA
All of these are known to be involved in aging so exposure to airborne particles may be accelerating aging.
Inflammation in the body is known to be linked to aging. It has recently become apparent that the stimulation of Aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhR) by air pollution leads to increase production of interleukin 33, which stimulates inflammation. These receptors are found on cells in organs that are in contact with air – the skin, the gut and lungs. The inflammation can exacerbate asthma could also potentially lead to accelerated aging.
A study before, during, and after the Beijing Olympics looking at air pollution. It found a change in 69 metabolites in the blood. Some of these changes would due to the breakdown of cells release of membrane components into the bloodstream. These can then turn into molecules that stimulate inflammation. The scientists also found an increase in antioxidants thought to be part of our body’s defense mechanism.
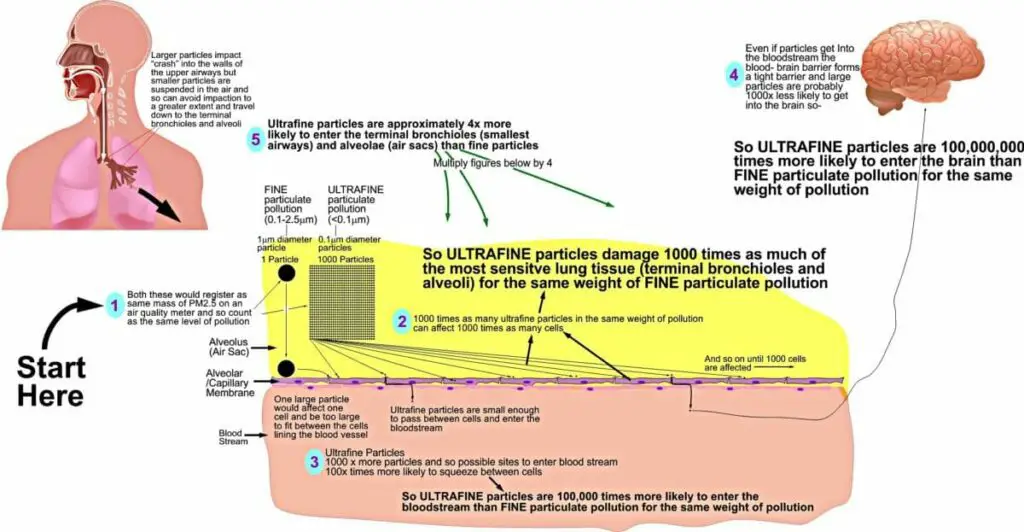
There is also an association between ultrafine particles and-
Aging/Age-Related Declines in Health Are Increased by Particulate Air Pollution
Those people exposed to more traffic related air pollution experience 3 years more decline in health status and those exposed to less. So traffic related applications seen as accelerating the usual age-related decline in health.
Telomeres shorten as we age, and so shorter telomeres are taken as a sign of increased aging. Babies born to mothers you are exposed to air pollution have 9% shorter telomeres in their blood cells. They also have 16% shorter telomeres from cells in their placenta. Preschool children who live near roads or have more roads near their houses have shorter telomeres. Traffic related pollution was also associated with shortened telomeres in children and adolescents in California. Similarly, in adults long-term exposure to small particles (PM 2.5) was linked to shorter telomeres.
Shortened telomeres have been linked to a shorter lifespan, bone marrow failure, pulmonary fibrosis and liver disease.
Also, the EPA regard air pollution as a factor in lung aging-please see EPA infographic (1st illustration above).
As mentioned above, particles in the air induce oxidative stress in skin. They also promote external signs of skin aging. Ozone at levels found in urban areas decreases sirtuin 3 activity in epidermal skin cells. Sirtuins are involved in the cellular biology of aging, with sirtuin 3 located in the mitochondria – the main powerhouses of our cells. So by inhibiting sirtuin’s ozone can be thought of as increasing the rate of aging. Another study also found that skin aging is increased by exposure to traffic related air pollution.
As outlined in the section on children epigenetic aging was speeded up by exposure to indoor air particles, in a study from Europe.
So, there is scientific evidence that air pollution influences at least 4 cellular mechanisms of aging. Also, for skin more exposure to air pollution leads to the appearance of more aged skin.
Premature Death is Linked to Particulate Air Pollution
There is evidence of a link between fine particle air pollution and premature death, even at particle counts below the current EPA standard of 12ug/m3. A study of 6 US cities found that particulate air pollution was linked to death, particularly from lung cancer and cardiopulmonary causes. Following the Clean Air Acts, a decrease in mortality has been seen. It has been calculated that for each 10 mcg/m³ decrease in PM 2.5 pollution, people live in an additional 0.6 years. In another study of 500,000 Americans, followed over 9 years, it was found that mortality increased 3% per 10 mcg/m³ of PM 2.5 exposure.
Interestingly, although total mortality increased 3%, cardiovascular mortality increased 10% but the increase in mortality from respiratory disease was not significant. This is surprising and implies that the particles entering the bloodstream are more lethal than those simply deposited in the lungs.
A study of 1/2 million people from the UK biobank study used two normal statistical methods as well as a machine learning algorithm to predict mortality. The machine learning algorithm turned out to be better at predicting mortality than either of the conventional statistical methods. It’s 9th most important variable in making the prediction was air pollution.
Air pollution in the United States causes 100,000 deaths per year. Half of these deaths are from PM 2.5 generated particles from electricity generation and cars. However, woodstoves and livestock are also a big problem. For instance, ammonia generation by livestock from manure can cause formation of PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere and these are responsible for 20,000 deaths per year in the US. In the US it is estimated that national life expectancy is decreased by about 2 months because of air pollution.
Another study in 2021 from Harvard found that mortality from particle pollution had been underestimated. It found a particular problem in the China and India but also in the eastern United States, anywhere where large amounts of fossil fuel are burned. Particulate pollution contributed to 17% of deaths in the UK and 13% of deaths in the US.
In the EU in 2015, it is estimated that 659,000 deaths were caused by air pollution. This reduced life expectancy by 2.2 years. It is estimated that China could increase life expectancy by almost 3 years by meeting WHO standards for air pollution. Worldwide it is estimated that 8.8 million deaths are caused each year-more than smoking, which causes 7.2 million deaths!
So which types of particles are particularly problematic? One study looked at the metal particulate matter present in samples of moss and then correlated this with mortality. The participants exposed to higher atmospheric concentrations of metals due to human activity had a higher mortality. So metal particles may be especially problematic.
It seems even premature death is one of the health problems from air pollution.
Genetic Aging is Linked to Particle Exposure
The genetic age of a person can be assessed by looking at epigenetic changes in the DNA. Epigenetic changes are changes where different molecular groups, usually methyl or acetyl groups attached to or removed from DNA. The degree of methylation of our DNA changes with age. By measuring methylation of DNA it can be assessed how old someone is and when they are likely to die, Horvarth’s “grim age” DNA clock is the most accurate.
Particle exposure in children has been linked to accelerated DNA aging in this study.
Rural Areas Can Have Significant Air Pollution
One study found the PM 2.5 amount was as high in rural Washington State compared to urban Seattle. This was associated with more asthma symptoms for children in the rural area. Large-scale animal feeding operations can cause pollution with chemicals such as ammonia in the atmosphere, causing small particle formation which leading to decreased lung function in children with asthma. Corn production also produces ammonia, which leads to increase production of small particles in the air. It is thought be linked to 4300 premature deaths annually in the US. The monetary cost of this is thought to be $39 billion.
Subways Can Have Very High Concentrations of Pollution
A study on the London underground/subway showed that PM 2.5 concentrations in the subway were 15 times those of the surface roadside readings. The concentrations were greater than those in Beijing or Guangzhou. A typical daily commute can make up a significant proportion of someone’s daily exposure.
Wildfire Smoke is worse for the lungs than other types of particle pollution
Wildfire smoke increases the risk of respiratory problems more than other causes of PM2.5 fine particle pollution. For each 10 ug/m3 increase in fine particle pollution wildfire smoke caused a 1.3% increase in respiratory hospitalizations compared to a 1% increase for other fine particulate pollution. Fortunately, there are air purifier models that are extremely good at dealing with wildfire smoke, there is an article about them here.
Health Problems From Air Pollution Can be Caused by Short Term Exposure
Does mortality increase at levels well below current safe levels? The answer seems to be yes. This is based on a study in which low-level pollution exposures to air pollution were linked to an increased risk of death amongst the elderly. There was a continual increase even from approximately zero pollution and in fact the gradient of the care of his greatest at the lowest pollution. The steep gradient means that there is more change in death rate per unit air pollution. This seems to be a “smoking gun” of air pollution showing that there is no level of air pollution that is absolutely safe.
Air pollution is higher in Beijing than Los Angeles. Researchers looked at the changes in the blood of 26 subjects from Los Angeles, during and following a 10 week stay, in Beijing. They found that levels of PAH were increased 176-800% during the stay in Beijing. Serum antioxidants were lower, the levels of oxidized lipids were higher, and an inflammatory protein was increased by 100% when in Beijing. The levels returned to normal after 4 to 7 weeks back in Los Angeles.
Hospital admission after short-term exposure to PM 2.5 was assessed for 214 medical conditions in people aged 65 or older admitted to hospital in the United States. Admissions occurred with increased frequency for –
- Septicemia (41%)
- Fluid and electrolyte disorders (43%)
- Renal failure (32%
- Urinary tract infections (39%)
- Cardiovascular disease especially heart failure(68%), heart attack (29%) and cardiac rhythm disturbance (26%)
- Respiratory Disease especially pneumonia (63%) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (36%)
- Parkinson’s disease (19%)
- Diabetes
- Thrombophlebitis
- Thromboembolism
Figures in brackets indicate percentage increase
These associations occurred even at a PM2.5 concentration below WHO air quality guidelines.
Short-term air pollution is also been linked to an increased incidence of stroke.
HEPA Air Purifiers Reduces the Effects of Particle Pollution
In a study of 45 adults in 25 residential homes an air purifier was used in the main activity room and the residents bedroom. The HEPA filters were in place for one period and removed for another-the resident was not aware of whether or not the filter had been removed. The average reduction in particle count was 60% with the HEPA filters. 13 of the homes had woodstoves.
At the end of each 7 day period the function of small blood vessels was assessed and a marker of inflammation in the blood measured, C-reactive protein.
Reducing particle pollution with HEPA filters improved blood vessel function 9% and reduced CRP 33%. This was even without optimally effective particle reduction. The EPA recommend an 80% reduction but I think based on current data one should aim for a PM2.5 as close to zero as you can reasonably get given your home.
This establishes that removing particles from the air has meaningful beneficial health effects.
How do I Know if I Need an Air Purifier?
As a general rule if you live in the US you need an air purifier. This is because 98% of people, for which there are data, live in areas with an outdoor PM2.5 airborne particle level above the 2021 WHO standard of 5ug/m3. Then when you factor in the pollution actually created in your house and the fact that these WHO levels are likely too high in any case*, then almost everyone would potentially have better health breathing filtered air provided by an air purifier. This probably applies to almost all industrialised countries, unless you live in the very remote areas of the country.
*Mortality rises with PM 2.5 levels lower than the WHO cutoff.
Conclusion
Currently, the weight of the evidence is that air pollution damages many of our internal organs, including our brains. However, “air pollution” is set at an arbitrary mass of particles per volume of air. The evidence suggests that below this arbitrary number there are significant effects on our health. There is also the possibility the health affects of airborne particles may extend to aging in general, but especially in the skin and lungs which are in direct contact with the particles. Certainly air pollution also seems to be linked to premature death.
This therefore begs the question-if we all bought air purifiers and reduced our particle exposure by at least 80% would we in the end be fitter, more intelligent, happier, age more slowly and live longer? Logically we may well do, but there is a lack of long-term studies. So no one knows for sure. Obviously, with this lack of data on this point, no population wide recommendations can be made.
For most people, the starting point would be to buy an air quality meter to measure the air quality at home to see what the situation is this is an important starting point but unless the PM2.5 reading is zero you will need to consider whether you should get an air purifier.
People who can afford to do so may wish to buy air purifiers and live in an environment which is freer of particles – that is personal choice. There is currently no known health downside to breathing in fewer particles the only downside is the cost of the air purifier and the filters. If you do decide to live in an environment with fewer particles, I would suggest as well as buying air purifiers, also remodelling your HVAC system.
Related Posts
Healthier Home? Use your HVAC system as a dream whole home air purifier?-this article explains how you can remodel your HVAC system to enable better particle filtering
The Best HVAC Filter?-Time to Change Your Filter Technology-this article explains how you can use a custom HVAC filter to improve the qualitiy of care from your HVAC system